Astronomical Yearbook for 2024
DOI: 10.32876/AstroYearbook.2024
Preface
In the "Astronomical Yearbook" (AY) the ephemerides of the Sun, Moon, major planets and stars computed with the maximum precision in accordance with the resolutions approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) are published. The information is also given on various astronomical phenomena - lunar and solar eclipses, planetary configurations, rises and sets of the Sun and Moon, etc. The explanation, contained the examples, illustrates the possibility of the calculation of various ephemerides to any particular time and for the any observation place.
Since issue for 2004 the reform AY was carried out connected to change of ephemerical basis AY according to Recommendations XXIII-XXIV General assemblies (GA) IAU. In the course several years full replacement of theories of movement of major planets and the Moon, of the precession-nutation models, of the star catalogue is stage by stage made. The system of coordinates based on the new concept of "the non-rotating origin" is entered. Separate stages of reform are described in forewords and explanations to the Yearbooks on 2004-2008. Change of an ephemeris basis - replacement of the theory of EPM2004 by EPM2011/m created in IAA RAS, became the last stage of work.
Preparation of the AE-2024 ephemerides is based on the following data:
- The fundamental ephemerides of the Sun, the Moon and major planets are calculated on the theory EPM2011/m developed at IAA RAS. This theory present the movement of these objects with accuracy enough for the theoretical and practical applications. The differences between the theories EPM2011/m and DE405/LE405 in common use developed at the JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, USA) are less on the order than the accuracy of the data published in AY for these bodies.
- In accordance with the IAU2000 resolution the parameters of the nutation in longitude and declination are calculated under the IAU2000_R06 nutation theory (Note of IERS Conventions Center, 16 June 2009).
- The account of precession was carried out in the Lieske method of parameterization with values of polynomial coefficients corresponding the new precession model P03 resulted in the report of Working group of IAU on precession and the ecliptic (2006).
- Calculation the sidereal time is made with use "the Siderial Angle" and new expression for the equation of equinoxes accepted by "IERS Convention (2003)", and P03 precession theory.
- The shift of average pole J2000.0 relative to the pole ICRS is taken into account at calculation of elements of the precession-nutation matrix.
- Calculing the stars ephemerides the fundamental catalog FK6 was used. The ephemerides of the stars which have not in this catalog are based on the catalog HIPPARCOS. Both catalogues are in ICRS. Calculating the corrections for orbital movement of double stars "Fourth catalog of orbits of visual binary stars" WH-4 was used.
- The ephemeris data of the Yearbook are given in the classical concept of equinox. According to the recommendation XXIV GA IAU (resolution B1.7) the data connected with the new Celestial Intermediate Reference System (CIRS), and elements of a matrix of transition from ICRS to the celestial intermediate origin CIO and true equator of date are given.
All ephemeris data are calculated by means of the PS BOOKA edition package of a updated multi-purpose program complex the ERA-8 developed in IAA of RAS for the decision of problems of ephemeris astronomy. The updated program complex ERA-8 (Pavlov D.A., Skripnichenko V.I. First results of trial operation of the cross-platform version of ERA system // Works IAA of RAS, SPb.: Science, 2014. Vyp.30. Page 32-40) is included in program BOOKA system which is used for calculation of ephemerises for the IAA printing editions of RAS.
In "The Astronomical Yearbook for 2024" the calculation of the ephemeris data was carried out by following collaborators of the laboratory of astronomical yearbooks:
- the sidereal time, the ephemerides of the geocentric coordinates of the Sun, the ephemerides of the geocentric coordinates of the Moon, and coefficients of the Tchebyshev polynomials, the geocentric and heliocentric coordinates of the major planets, osculating elements of the planet orbits, the ephemerides of the position and velocity of the Earth in the barycentric reference system, the elements of the precession matrix and of the nutation matrix, the terms by reductions, the ephemerides for physical observations of the Moon, the phases of the Moon, perigee and apogee - N.I. Glebova;
- the seasons and precession values, the planetary configurations - N.I. Glebova;
- the data for the eclipses of the Sun and Moon - M.V. Lukashova;
- the data for the occultations of planets by the Moon - G.A. Kosmodamianskij;
- the ephemerides for physical observations of the Sun, planets and Saturn's rings - G.A. Kosmodamianskij;
- the times of rise and set of the Sun and Moon - M.V. Lukashova;
- the table of the corrections for the orbital motion of stars - N.I. Glebova, N.B. Zheleznov;
- the mean places of stars on epoch of the year, the apparent places of the tenday and circumpolar stars - N.I. Glebova;
- the tables for altitudes and azimuths of Polaris and the tables for latitude determinations from observations of Polaris - G.A. Kosmodamianskij;
- Earth rotation angle, Equation of the Origins, the CIP parameters, matrix elements for conversion from ICRS to CIO and true equator of date - N.I. Glebova;
The data control was carried out by N.I. Glebova, I.A. Lebedeva, and E.I. Sheldyaeva.
The explanation to the Yearbook is processed by N.I. Glebova, and N.B. Zheleznov. \ The additional information on algorithms of calculation of ephemerides published in AY is given in "The Explanatory Supplement to "the Astronomical Yearbook" ("Transactions of IAA of RAS", 2004, vol.10). The examples in the Explanation were carried out by N.I. Glebova, G.A. Kosmodamianskij, and M.V. Lukashova. The Explanation in the TEX was carried out by N.I. Glebova, M.V. Lukashova, and N.B. Zheleznov.
Since 1995 the publication of the "Astronomical Yearbook" was carried out by means of the "PUBLISHER" integrated environment (G.A. Netsvetaeva. PUBLISHER - integrated environment for support astronomical yearbook issue, Communications of IAA of RAS. 2010, в„–В 187) developed on the basis of the < SVITA > programming system (Netsvetaeva G.A., Novikov F.A., Pariyskaya E.Yu. System of automatic layout of table publications (SVITA) //Communications of IAA RAS. 1998. № 118).
The dummy of "The Astronomical Yearbook for 2024" was carried out by D.A. Ryzhkova.
Contents
| Preface | 3 | |
| Seasons, some constants | 5 | |
| Sidereal time | 6 | |
| Ephemeris of the Sun | 10 | |
| Rectangular equatorial coordinates of the Sun | 26 | |
| Aberration, parallax, mean longitude of the Sun, obliquity of the ecliptic, nutation in obliquity | 34 | |
| Mean longitude of the Moon, mean elements of the Moon's orbit and equator | 35 | |
| Ephemeris of the Moon | 36 | |
| Right ascension, declination and geocentric distance of the Moon | 52 | |
| Coefficients of the Tchebyshev polynomials, the Moon | 60 | |
| Phases of the Moon, perigee and apogee | 60 | |
| Heliocentric coordinates of the planets | 61 | |
| Osculating elements of the internal planets | 66 | |
| Osculating elements of the outer planets | 67 | |
| Ephemeris of Mercury | 68 | |
| Ephemeris of Venus | 76 | |
| Ephemeris of Mars | 84 | |
| Ephemeris of Jupiter | 92 | |
| Ephemeris of Saturn | 100 | |
| Ephemeris of Uranus | 108 | |
| Ephemeris of Neptune | 116 | |
| Ephemeris of Pluto | 124 | |
| Position and velocity of the Earth | 126 | |
| Precession and nutation | 127 | |
| Terms of reductions at 0h Terrestrial Time | 142 | |
| Eclipses | 150 | |
| Planetary configurations | 158 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of the Sun | 162 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of the Moon | 166 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Mercury | 174 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Venus | 182 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Mars | 186 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Jupiter | 194 | |
| Physical data for the Sun, Moon, and major planets | 201 | |
| Rotational elements of the planets | 201 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Saturn | 202 | |
| Saturn's rings | 208 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Uranus | 210 | |
| Ephemeris for physical observations of Neptune | 212 | |
| Times of sunrise and sunset for latitudes from +30В° through +70В° | 214 | |
| Times of moonrise and moonset for latitudes from +30В° through +70В° | 222 | |
| Abbreviations of names of constellations | 254 | |
| Abbreviations of names of catalogues | 254 | |
| Mean places of stars (J2024.5) | 255 | |
| Mean places of circumpolar stars (J2024.5) | 269 | |
| Mean places of stars (ICRS) | 270 | |
| Mean places of circumpolar stars (ICRS) | 284 | |
| Terms of reductions for 0h of sidereal dynamical time | 285 | |
| Second order terms of reductions | 293 | |
| Apparent places of stars | 297 | |
| Apparent places of circumpolar stars | 480 | |
| Tables for latitude determinations from observations of Polaris | 574 | |
| Table for altitudes and azimuths of Polaris | 579 | |
| Earth rotation angle and Equation of the Origins | 582 | |
| Celestial Intermediate Reference System | 586 | |
| Matrix elements for conversion to CIRS | 590 | |
| Auxiliary tables | ||
| I. | Julian dates | 599 |
| IIa. | Conversion of mean time to sidereal time (with accuracy 0.01s) | 604 |
| IIb. | Conversion of sidereal time to mean time (with accuracy 0.01s) | 605 |
| IIIa. | Conversion of mean time to sidereal time (with accuracy 0.001s and 0.0001s) | 606 |
| IIIb. | Conversion of sidereal time to mean time (with accuracy 0.001s and 0.0001s) | 607 |
| IVa. | Conversion of minutes and seconds to fractions of degree and back | 608 |
| IVb. | Conversion of decimal parts of degree to minutes and seconds and back | 609 |
| V. | Conversion of arc to time | 610 |
| VI. | Conversion of minutes and seconds to parts of hour | 610 |
| VII. | Conversion of hours, minutes and seconds to parts of day | 611 |
| VIIIa. | Elements of PE-90 Earth's spheroid. Calculation geocentric coordinates of the Earth's surface points | 612 |
| VIIIb. | Elements of IUGG Earth's spheroid. Calculation geocentric coordinates of the Earth's surface points | 613 |
| IX. | Coefficients of Bessel's interpolation formula | 614 |
| X. | Refraction (precision 1") | 615 |
| XI. | Refraction (precision 0.1") | 616 |
| Explanation to Astronomical Yearbook for 2024 | ||
| 1. | General remarks | 617 |
| 2. | Interpolation | 626 |
| 3. | Sidereal time | 629 |
| 4. | Transition from One Time Measure System to Another | 630 |
| 5. | Fundamental ephemeris of the Sun, the Moon, and major planets | 634 |
| 6. | Ephemeris of the Sun: the equatorial and ecliptical coordinates | 636 |
| 7. | Rectangular equatorial coordinates of the Sun | 640 |
| 8. | Mean elements of Sun's orbit. Mean elements of Moon's orbit and equator | 641 |
| 9. | Ephemeris of the Moon. Coefficients of the Tchebyshev polynomials. Phases of the Moon, perigee, apogee | 641 |
| 10. | Heliocentric coordinates of planets. Osculating elements | 643 |
| 11. | Ephemerides of the major planets | 644 |
| 12. | Position and velocity of the Earth. precession and nutation | 646 |
| 13. | Terms of reductions | 648 |
| 14. | Eclipses | 649 |
| 15. | Planetary configurations and other astronomical phenomena | 653 |
| 16. | Ephemeris for physical observations of the Sun | 653 |
| 17. | Ephemeris for physical observations of the Moon | 654 |
| 18. | Planetocentric and planetographic coordinates of the Earth and the Sun | 655 |
| 19. | Ephemeris for physical observations of planets | 657 |
| 20. | Saturn's rings | 658 |
| 21. | Times of rise and set of the Sun and Moon | 659 |
| 22. | Mean places of stars | 660 |
| 23. | Apparent places of stars | 662 |
| 24. | Apparent places of circumpolar stars | 670 |
| 25. | Tables for latitude determinations from observations of Polaris | 673 |
| 26. | Earth rotation angle and Equation of the Origins | 674 |
| 27. | Parameters of the Celestial Intermediate Reference System | 675 |
| 28. | Matrix elements for conversion from ICRS to CIRS | 675 |
| 29. | The application to the Astronomical yearbook for 2022 | 677 |
| Index | 678 |
Eclipses
| Marth 25 | Penumbral lunar eclipse | Description | 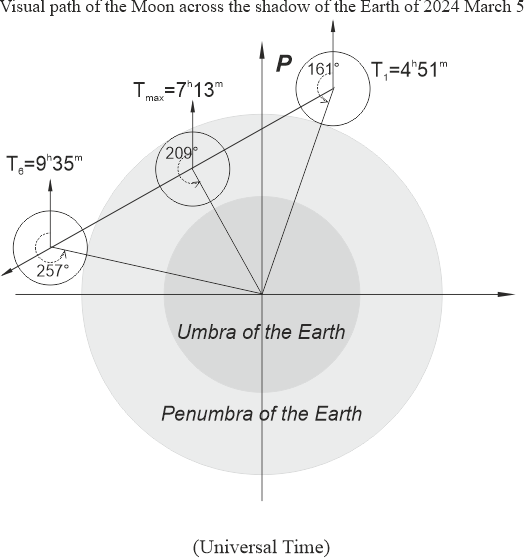 |
Visual path (for printing) |
| April 8 | Total solar eclipse | Description | 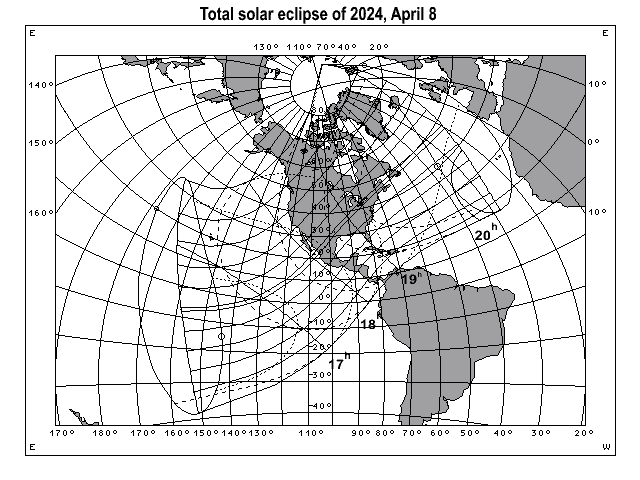 |
Map (for printing) |
| September 18 | Partial lunar eclipse | Description | 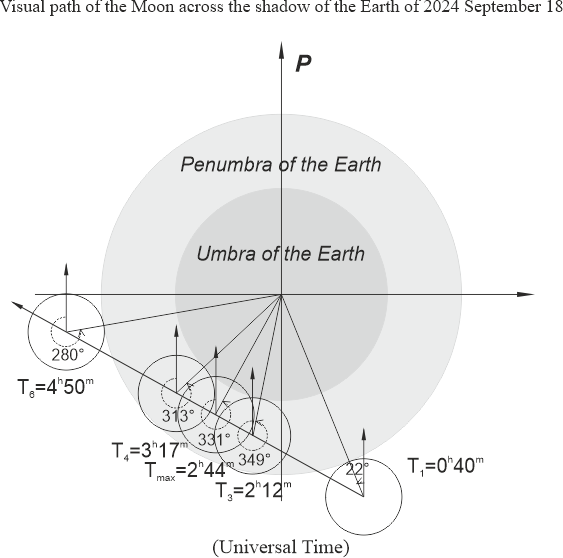 |
Visual path (for printing) |
| October 2 | Annular solar eclipse | Description | 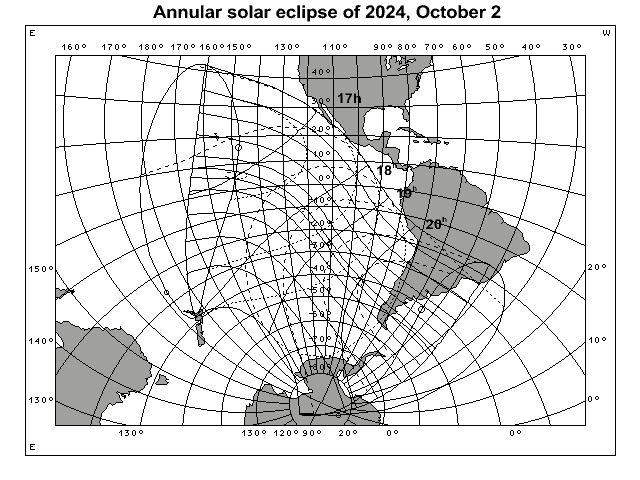 |
Map (for printing) |