Venus
The second planet from the Sun and the sixth largest planet in the solar system, belonging to terrestrial planets. Venus has a dense atmosphere that blocks visible light, but coming closer to the Earth than other planets allows us to study its surface using ground-based radar astronomy methods.
Characteristics
| Mean radius | 6051.8 km |
| Rotation period | 243.023 d |
| Axial tilt | 177.36° |
Radar scattering properties
SC/OC |
0.06 [1] |
| Radar albedo | 0.1 [1] |
Observation Schedule
| Date | Window, UT | Receiver |
Transmitter |
Frequency, MHz |
λ, cm |
Ptx, kW |
R, au |
RTT, sec |
SNR/RTT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 Jan 22 | 09:55 - 10:35 | RT-13 (Sw) | CCN [2] | 7190.0 | 4.2 | 8 | 0.29355 | 293 | 54 |
Echo power spectrum
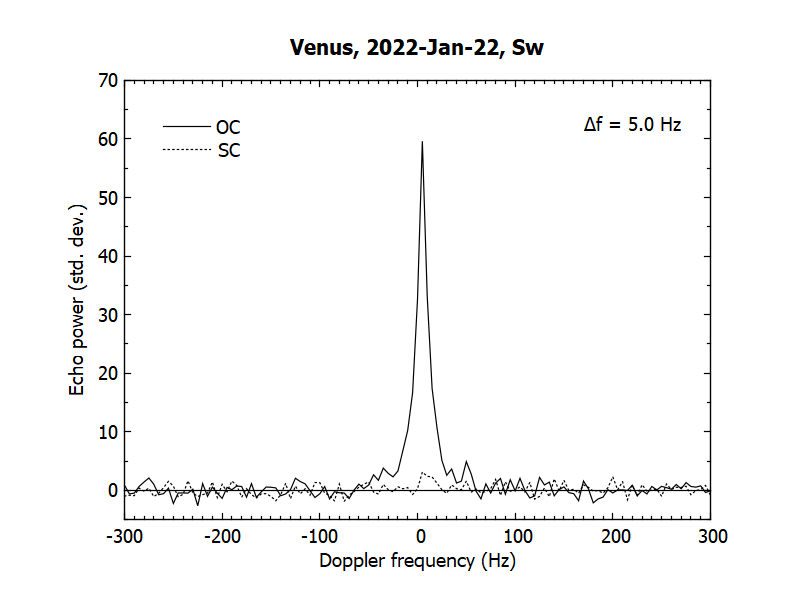
Bistatic CCN/RT-13 continuous wave echo power spectra of the Venus surface obtained at Svetloe observatory on January 22, 2022 from 09:55 to 10:35 UT. Solid and dashed lines denote echo power in the opposite circular (OC) and same circular (SC) polarizations as that of the transmitted wave. The obtained power spectra were used to estimate the сircular polarization ratio of ~0.06 as well as the radar albedo of ~0.1.
Remarks
Yu. Bondarenko et al., 2022.
We thank the National Commission on Space Activities of Argentina (CONAE) and the technical staff at CLTC-CONAE-NEUQUEN station for the help with the radar observations.